Page 28 - Environmental_Circular Economy
P. 28
28
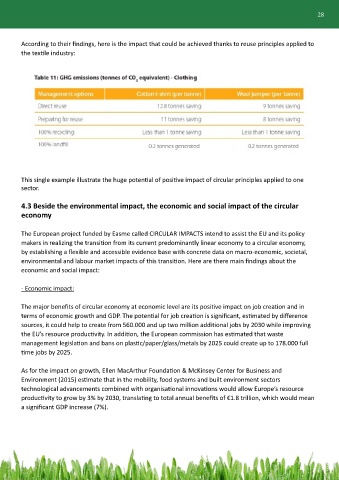
According to their findings, here is the impact that could be achieved thanks to reuse principles applied to
the textile industry:
This single example illustrate the huge potential of positive impact of circular principles applied to one
sector.
4.3 Beside the environmental impact, the economic and social impact of the circular
economy
The European project funded by Easme called CIRCULAR IMPACTS intend to assist the EU and its policy
makers in realizing the transition from its current predominantly linear economy to a circular economy,
by establishing a flexible and accessible evidence base with concrete data on macro-economic, societal,
environmental and labour market impacts of this transition. Here are there main findings about the
economic and social impact:
- Economic impact:
The major benefits of circular economy at economic level are its positive impact on job creation and in
terms of economic growth and GDP. The potential for job creation is significant, estimated by difference
sources, it could help to create from 560.000 and up two million additional jobs by 2030 while improving
the EU’s resource productivity. In addition, the European commission has estimated that waste
management legislation and bans on plastic/paper/glass/metals by 2025 could create up to 178.000 full
time jobs by 2025.
As for the impact on growth, Ellen MacArthur Foundation & McKinsey Center for Business and
Environment (2015) estimate that in the mobility, food systems and built environment sectors
technological advancements combined with organisational innovations would allow Europe’s resource
productivity to grow by 3% by 2030, translating to total annual benefits of €1.8 trillion, which would mean
a significant GDP increase (7%).