Article by MEUS
A sustainable economy is guided and constrained by ecological, social, and economic principles. In other words, to achieve sustainable development, there must be economic progress, social justice, and preservation of the environment. Therefore, sustainability is made up of three pillars: economy, society, and the environment. These principles are also informally referred to as profit, people, and planet.
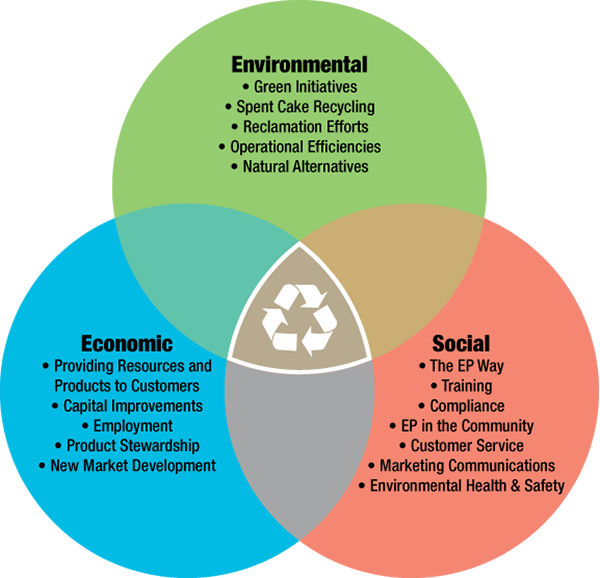
Economic
It measures the sustainability from the viewpoint of the consumer-led culture treating finite resources of nature as an income that will result in the aversion of natural crisis. Sustainability should generate economic wealth in a local, regional, and global framework that stimulates financially possible and profitable development, maintaining the base of natural resources and their conservation.
Social
Sustainability answer to a need to improve the quality of life of the population as a whole and to seek for social cohesion (intragenerational equity), as well as to preserve natural capital and the quality of the environment for future generations (intergenerational equity). It is based on the maintenance of the social and cultural network, of the capacity to maintain common interests through democratic and non-exclusive channels. This should be achieved through changing personal and collective attitudes and practices where people care about others and value social justice, education, health, peace, and tranquillity, improving and maintaining the global quality of human life over generations.
Environmental
Consideration of environmental protection is an integral part of the development process. It involves incorporating the environmental variable with an ecological approach in each one of the different sectorial policies and actions: rational use of natural resources, minimizing the production and dangerousness of waste, contributing to the prevention and solution of global environmental problems, conserving and restore degraded ecosystems and natural spaces, among others. Sustainability means the compatibility between human activities and the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystems. The levels of exploitation of natural resources are maintained without reaching its limit (carrying capacity) and without leading to a decrease in the resource in its essence. It is intended to avoid the depletion of non-renewable, difficult, or slowly renewable resources; in addition to avoiding the generation of waste and polluting emissions.
But what is our current economic model? We currently have a linear economy model, which has hardly changed since the beginning of industrialization. It has been based and is based on the pattern of “extract, produce and dispose of”, that is, companies extract the raw materials they need, use them to manufacture and offer products and services so that the end-user finally discards them when they are they are not useful to them. And, as we know, the current linear economic model of extracting, producing, and disposing without considering the most basic aspects of this sustainability, is no longer viable from an environmental point of view, nor an economic-social point of view.
The world has become globalized and, it is evident that, given the enormous environmental pressure exerted by human activity on the planet, solutions must be proposed that seek and ensure the sustainability of all resources. And it must be done urgently.
This change is not only possible, but also necessary.
We must be able to know, define and apply, in a strategic way, all those activities, initiatives and models, within the economic and social sphere (1) Aimed at minimizing the use of raw materials that are produced in the most efficient way possible, using renewable energies and extending the useful life of products and food, and (2) that they maximize the reuse of waste through its recovery or reuse as initial raw material.
Are you interested in this topic? Learn more about sustainable consumption and sustainable action for youth thanks to our SUSTRAINY European Project: https://sustrainy.erasmus.site/
